It depends to a large extent on the application and therefore also on the application period of the finished product. Evaluation and testing within a risk management process
E3609-70 Iso 10993-5 -10 Compliant Epdm O-rings Parker O-rings O-ring Products United Seal
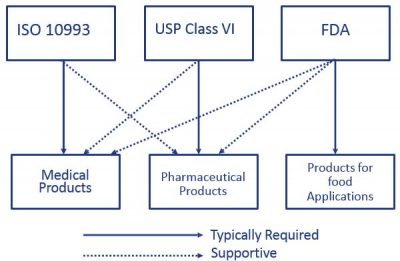
Both iso 10993 and usp class vi define testing requirements for biocompatibility, the ability of a material to perform a desired function without causing adverse effects on the human body.

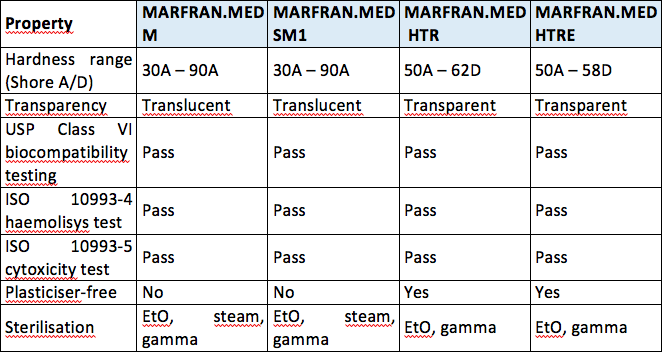
Usp class vi vs iso 10993. Unlike other rubber standards, there’s no one standard that engineers use for an approval. Usp class vi versus iso 10993 search and take a look to page 8 of the ensinger_medical_brochure_for_2006. In fact, usp class vi has been largely superseded since the release of iso 10993 in 1995.
Though not a limited series of tests, some biocompatibility requirements for medical devices may exceed the testing performed in usp class vi. Rob pruyn august 5, 2020 custom products, medical devices, molding services Though not a limited series of tests, some biocompatibility requirements for medical devices may exceed the testing performed in usp class vi.
The fda requires testing of finished devices, however, the demonstration of biocompatibility of materials according to usp class vi standards is provided as an aid to. The materials listed below are ideal for: In order to pass the class vi standards, the product/material must exhibit a very low level of toxicity by passing all the tests requirements when tested according to iso 10993.
Usp class vi biocompatibility testing: The picture should make clear the common part of the two regulations. The two main testing standards used today include usp class vi biocompatibility testing and iso 10993 biocompatibility testing.
Take an astm d2000 call out. 3d printing of one day crown prep guides. However, class vi also requires subacute toxicity and implantation effects, which are not required for many categories of iso 10993.
For example, usp class vi requires an intracutaneous irritation test, which is also required for iso 10993 compliance. Pharmacopeial convention (usp) that regulates standards for healthcare technologies, medications, food ingredients, polymers, as well as plastics used for. Most applications are fairly benign to elastomers.
To begin, let us address just what biocompatibility is. However, class vi also requires subacute toxicity and implantation effects, which many iso 10993 categories do not. We carry a wide range of materials from the world’s top medical resin suppliers, including usp class vi and iso 10993 certified biocompatible resins with full fda master file support.
Usp class vi testing is only one standard of biocompatibility, however. Meaning, what is the risk of my materials and processes to the patient? Class vi and iso 10993 are recommendations for testing based on the use of the final device.
This testing is devised by the u.s. A rubber compound has set physical parameters it needs to meet. Our portfolio approach offers the most expansive selection of medical resin materials in the industry, balancing performance, cost.
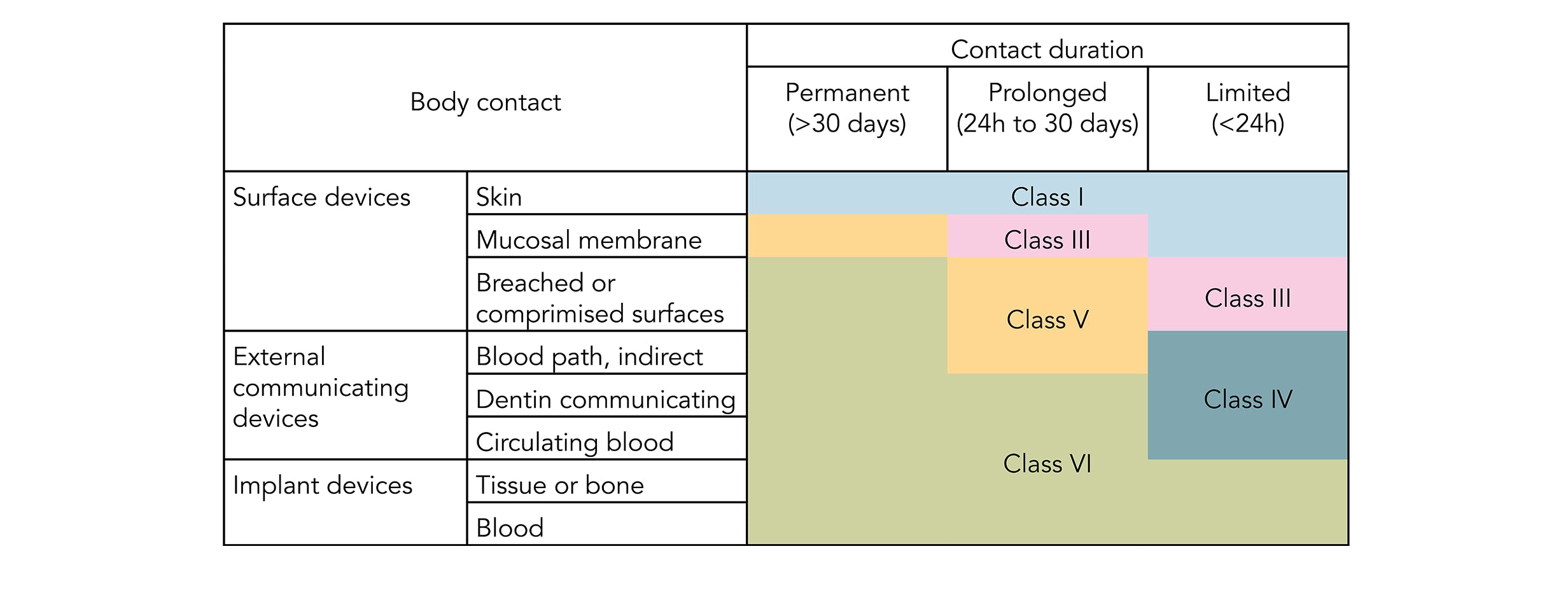
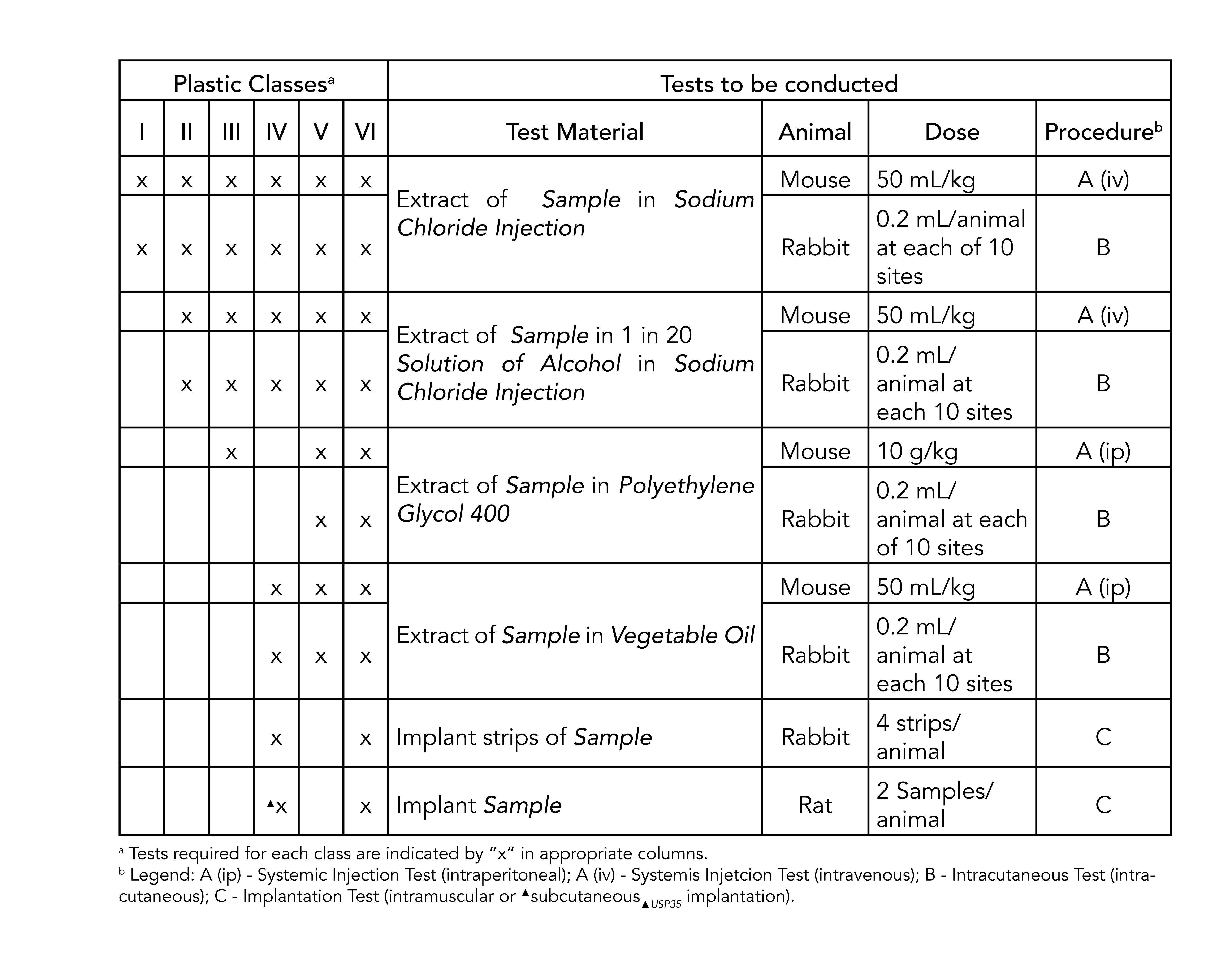
The most stringent, class vi, requires three types of tests: Class vi and iso 10993 are recommendations for testing based on the use of the final device. 3d printing of dental and orthopedic surgical guides;
Ep 3.1.9 ( ep ): That said, the lack of risk assessment in usp class vi can be a problem. Iso 10993 and risk iso 10993 is intended as a guidance to determine the potential biological risks arising from the use of medical devices.
Iso 10993 is designed for medical products that remain permanently or for a very long time in the human body, so for shorter applications, a usp class vi or even a lower usp class certification is often sufficient. As an example, usp class vi requires an intracutaneous irritation test, which is also required for iso 10993 compliance. It also misses required tests associated with other categories.
What is the difference between usp class vi and iso 10993? Medical molding and biocompatible rubber. Typically, the terms usp class vi or iso 10993 materials are used.
This post will take a deeper look at what biocompatibility is and how it is defined by the international standards organization. In addition to subacute toxicity and implantation effects, class vi also requires subacute toxicity and implantation effects, which are not required for many. Evaluation and testing within a risk management processfor example, technical polymers medical grades have dedicated manufacturing locations, which is not the case for standard grades.for the purpose of the iso 10993 family of.
Iso 10993 usp class vi demands an intracutaneous irritation test. Usp class vi vs iso 10993. However, some applications such as implantable devices are extremely complicated.
Ep 3.1.9 without appearance of solution inner diameter outer diameter wall thickness dow corning silastic® iso fda usp ep wacker iso fda usp (ep) mm mm mm ref ref 0,31 0,64 0,17 45630101 45634140 0,51 0,94 0,22 45630102 49300528 0,64 1,19 0,28 45630103 45634142 Both iso 10993 and usp class vi define testing requirements for biocompatibility, the ability of a material to perform a desired function without causing adverse effects on.
Biocompatibility Of Plastics Zeus
2
Material Selection Medical Injection Molding - Xcentric Mold
Bioblog Usp Class Vi - Venair

What Is Iso 10993 How Is It Different From Usp Class Vi - Ppt Download
Brilliant Mind The World Of Tubing For Medical Use - Medical Plastics News
Bioblog Usp Class Vi - Venair

What Is Iso 10993 How Is It Different From Usp Class Vi - Ppt Download

Biocompatible 3d Printing Explained

Bioblog Usp Class Vi - Venair

Understanding Food-grade Vs Biocompatibility For Medical Device Materials - Medical Product Outsourcing

Iso 10993 Vs Usp Class Vi Medical Molding And Bicompatible Rubber The Rubber Group
Biocompatibility Of Plastics Zeus
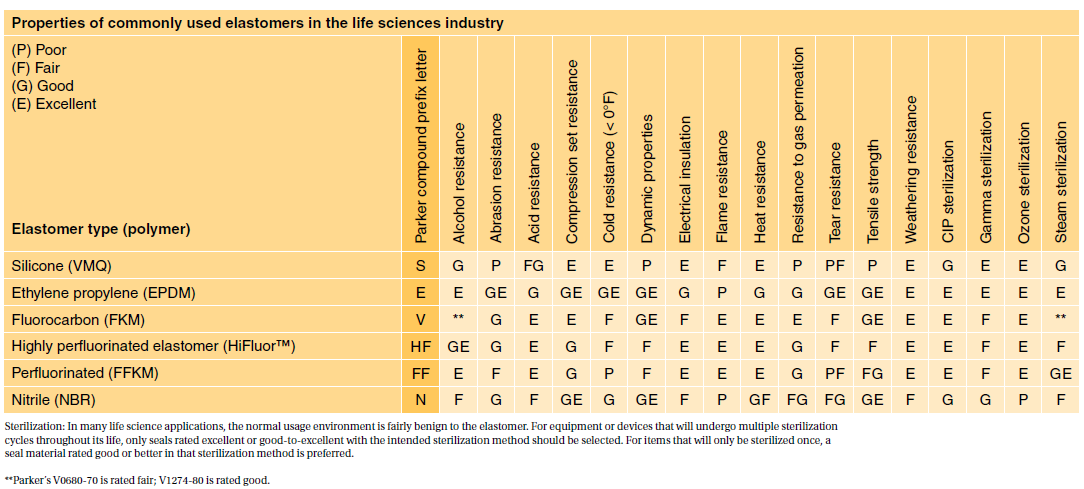
Fda And Usp Class Vi O-rings

Duraform Pa Certification - Usp Class Vi Iso 10993 And Food Contact
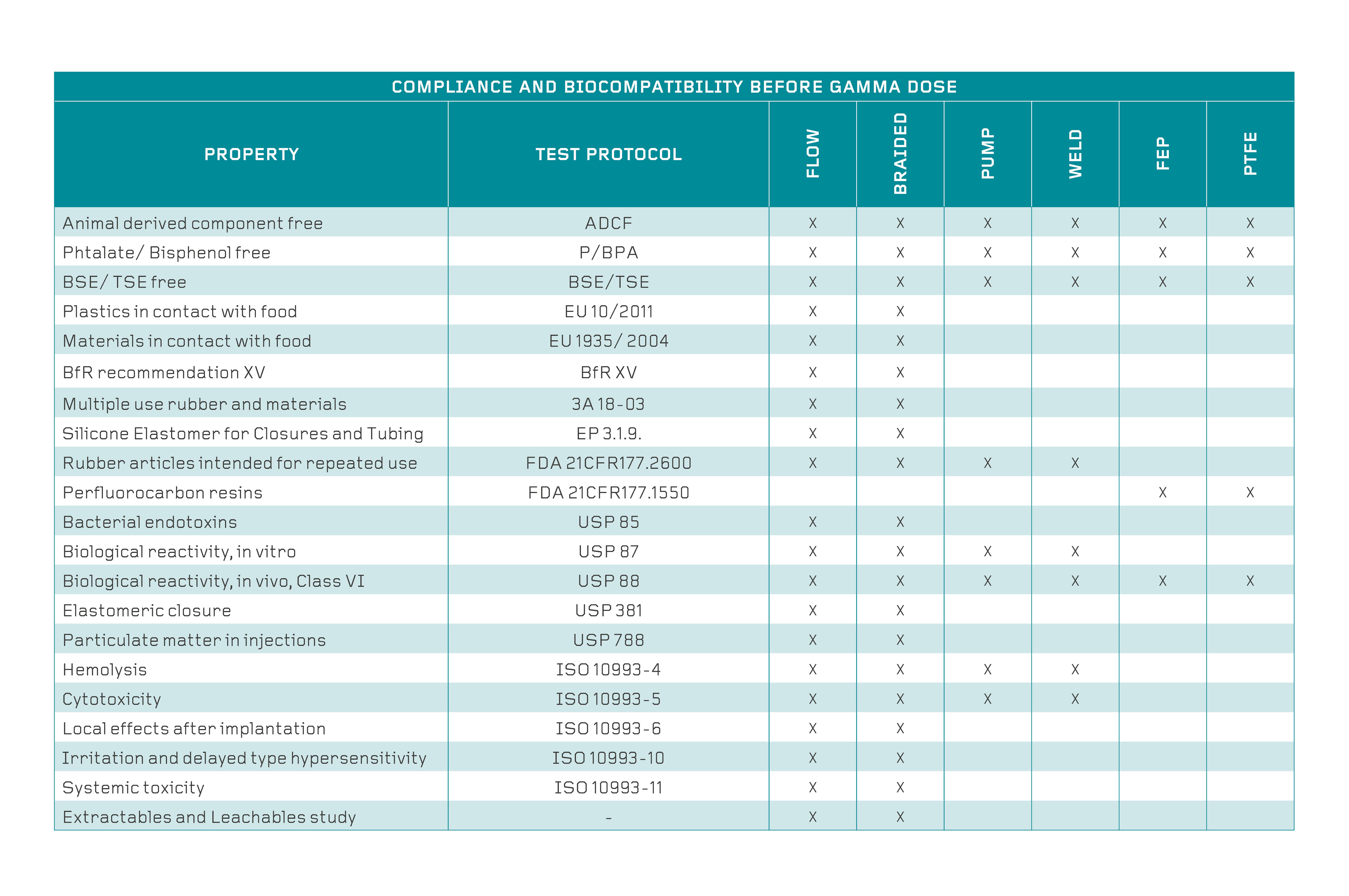
Bioblog Usp Class Vi - Venair
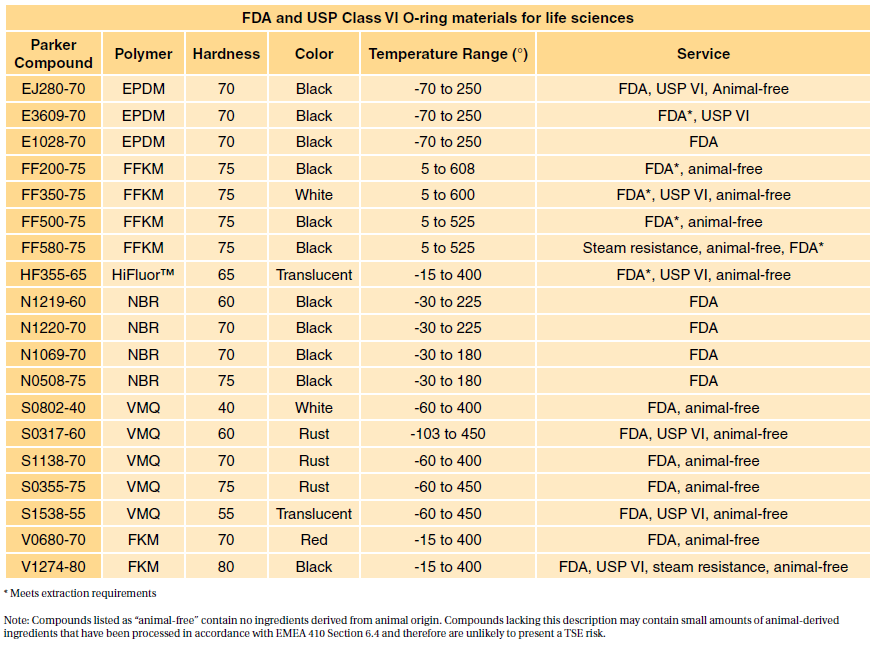
Fda And Usp Class Vi O-rings

Regulatory Guidelines For Biocompatibility Safety Testing Mddionlinecom
2